What Term Is Used When Describing Characteristics of Lava Flow
1 the presence of fractures that indicate of rapid cooling the penetration of water andor the presence of non-horizontal cooling surfaces. This morphology is are commonly known as fine-aa Jones 1943 semi-hoe Malin the primary basis for classification of lava flows when rheological 1980 or toothpaste lava.

Panoramic View Of The Source Areas Of The Lava Flows Studied Here Lava Download Scientific Diagram
Blocks are fragments of pre-existing.

. Pahoehoe is also known as ropy lava and it has several more varieties named entrail festooned filamented sharkskin shelly etc 4. The liquid lava flowing beneath a thin still-plastic crust drags and wrinkles it into tapestry-like folds and rolls resembling twisted rope. ꦮꦭꦲ is a violent type of mudflow or debris flow composed of a slurry of pyroclastic material rocky debris and water.
Helens a rapid mass movement that included fragmented cold and hot volcanic rock water snow glacier ice trees and some hot pyroclastic material. This lava forms blocks too and its surface is also flat and irregular. Pahoehoe lava flows are fed almost wholly internally.
In the concept of mineralogy or geology in the much broader sense two terms are commonly used to describe the characteristics of rocks and also lava. The top layers of these flows are composed of broken lava blocks. Pyroclastic debris ranges in size from ash to lapilli to larger pieces termed bombs.
As the upper surface of the lava cools and becomes rock it is continually ripped apart by the moving molten lava inside the flow. This relatively fast flow of volcanic ash and lava can cause a lava tube to form which permits the volcanos lava to flow even faster unimpeded along the easiest downward direction. Pieces of the rocky surface are broken rolled and tumbled along as the lava flow moves.
Rhyolites erupt from the Earths surface at temperatures of 1382 to 1562 degrees Fahrenheit. Pyroclastic debris forms when bodies of lava are shot into the atmosphere and cool during flight to form volcanic glass. Lava Flow Hazards Lava flows generally travel at slow speeds.
Its peculiar name comes from Hawaiian and means rocky with rough lava. But when basalt lava flows are confined within a channel or lava tube on a steep slope the main body of the flow can reach velocities 30 kmh 19 mph. The main term used to describe the characteristic of magma flow is viscosity.
These terms are mafic and felsic. A rapid and unusually sudden sliding or flowage of unsorted masses of rock and other material. Total deaths from flows since 1600 ad is about 900.
The material flows down from a volcano typically along a river valley. As applied to the major avalanche involved in the eruption of Mount St. The reason for such is the.
A lahar ˈlɑːhɑːr from Javanese. Aa lava flows have a very rough rubbly surface because of their high eruption rates. Lava is magma once it has been expelled from the interior of a terrestrial planet such as Earth or a moon onto its surface.
The most active area of the flow is the core which is much denser than the rough surfaces at the top of. Lava flows are streams of molten rock that pour or ooze from an erupting vent. This magma has a low viscosity which allows for gases to escape the volcano and for the lava flows to erupt calmly and predictably.
Best known examples of pahoehoe lava flows are from the Big Island of Hawaii and the term pahoehoe itself just as aa originates from the Hawaiian language. Pahoehoe lava flows are characterized by smooth gently undulating or broadly hummocky surfaces. Pāhoehoe lava has the following characteristics.
The identification of past lava-ice interaction is accomplished using specific features such as. And 2 unusually great lava flow thicknesses that show confinement or ponding against now non-existent walls implied to have been glacial. When finally cooled to a solid aa lava flows look like a jagged heap of loose rock.
Aa pronounced ah-ah is a Hawaiian term for lava flows that have a rough surface. Such flows will overlap one another and typically move less than a few meters per hour. The word derives from a composite of the chemical symbols for Magnesium Ma and Iron Fe.
Lava may be erupted at a volcano or through a fracture in the crust on land or undersea usually at temperatures from 800 to 1200 C 1470 to 2190 FThe volcanic rock resulting from subsequent cooling is also often called lava. This causes much confusion. Has a low volume flow rate Has a low flow rate velocity Forms lava tubes Has many flow channels Has thin flow units 02-2 meters or 07 to 6 feet Has lower viscosity and.
Tephra is a general term for fragments of volcanic rock and lava that are blasted into the air by explosions or carried upward by hot gases in eruption columns or lava fountains. Viscous dacite and rhyolite flows often form steep-sided mounds called lava domes over an erupting vent. Nuee ardente French for glowing cloud is another term used to describe a lava flow.
Viscosity is how thick a fluid is. Lava domes often grow by the extrusion of many individual flows 30 m 100 ft thick over a period of several months or years. Buildings and other structure of course are totally.
One of their distinct characteristics is the smooth appearance and high silica content. When used to describe the characteristics of lava mafic lava would mean that it is runnier or more viscous as opposed to the felsic lava. Since there is little rock in the shield lava flow as compared with other volcano types it moves at a faster rate which is caused by its low viscosity.
Mafic is a term used to describe the densest lava flows. These types of lava are related to the previous category up to the point that some classifications unify these two groups in one. Molten lava flows are relatively high-viscosity liquids and most of them advance slowly a few metres per minute to less than a metre per day.
The crystals are formed depending on the speed of the lava as well as the cooling period when it reaches the surface. The sharp and rugged surface of a hardened aa flow makes for treacherous and slow walking conditions. Pyroclastic flows which are low-viscosity fluidized mixtures of hot but solid volcanic fragments and hot gas are often described in newspaper accounts as lava flows.
These transitional lava flows morphology of a lava flow after solidification. Lava is erupted during either nonexplosive activity or explosive lava fountains. A fluid that is viscous is thick and.
Up to 10 cash back By far the most commonly used terms to describe lava surfaces today are not descriptive but instead are merely words specifically the Hawaiian words aā rough brecciated basalt lava and pāhoehoe smooth glassy basalt lava plus block lava thick brecciated lavas that are typically more silicic than basalt. You can decide whether a lava flow consists of pāhoehoe or ʻaʻā lava based on the following characteristics. Lava is molten rock flowing out of the volcano in liquid state and cooling and solidifying on the ground.
In lavathe Hawaiian names pahoehoe and aa or aa. Typical Hawaiian flows move at about 025 mileshr or about 6 milesday Consequently it is possible to avoid most flows resulting in very little loss of life.
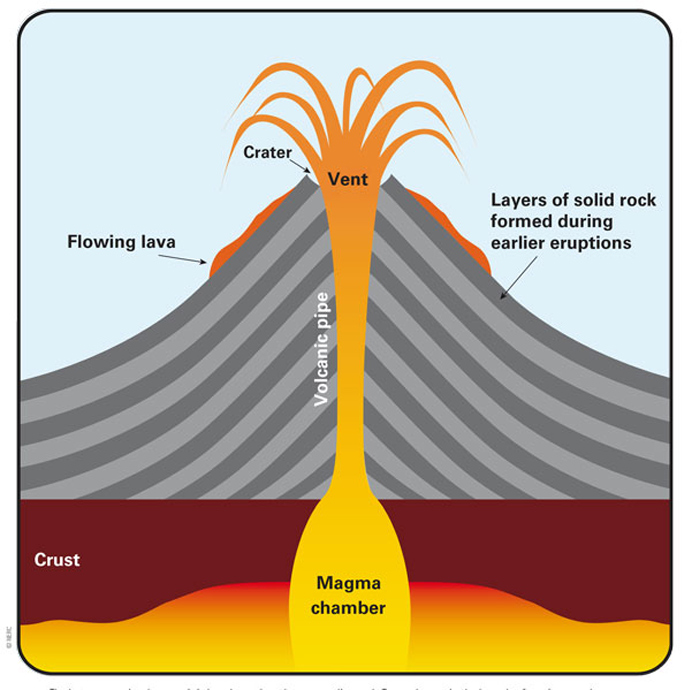
Types Of Volcano British Geological Survey

Lava Flow Map Of 2017 2018 And 2019 Lava Flows On A 2015 Shaded Relief Download Scientific Diagram

Pin By The Kineo School On Journey Erosion Paper Models Describe Me Geologists
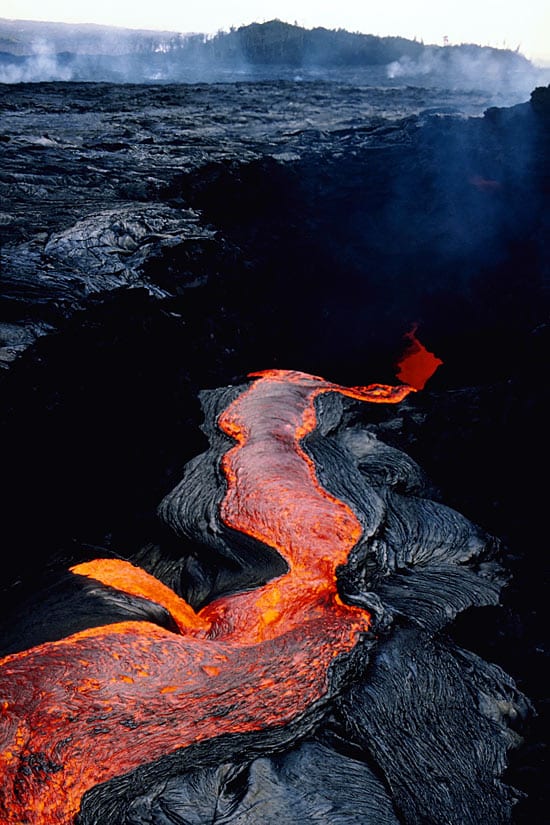

Lava Flows Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution

Lava Types Composition Temperature Facts Britannica

Definition Of Effective Thickness Dh Of Lava Flow It Is Possible To Download Scientific Diagram

What Term Is Used When Describing Characteristics Of Magma Flow Lisbdnet Com

Simplified Definition Of Lava Types And Their Morphology Note That All Download Table

Comments
Post a Comment